classical problems of synchronization as examples of a large class of concurrency-control problems. In our solutions to the problems, we use semaphores for synchronization, since that is the traditional way to present such solutions. However, actual implementations of these solutions could use mutex locks in place of binary semaphores.
These problems are used for testing nearly every newly proposed synchronization scheme. The following problems of synchronization are considered as classical problems:
1. Bounded-buffer (or Producer-Consumer) Problem, 2. Dining-Philosophers Problem, 3. Readers and Writers Problem, 4. Sleeping Barber Problem
These are summarized, for detailed explanation, you can view the linked articles for each.
- Bounded-buffer (or Producer-Consumer) Problem:
Bounded Buffer problem is also called producer consumer problem. This problem is generalized in terms of the Producer-Consumer problem. Solution to this problem is, creating two counting semaphores “full” and “empty” to keep track of the current number of full and empty buffers respectively. Producers produce a product and consumers consume the product, but both use of one of the containers each time.
- Dining-Philosophers Problem:
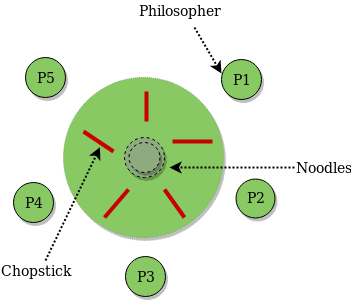
The Dining Philosopher Problem states that K philosophers seated around a circular table with one chopstick between each pair of philosophers. There is one chopstick between each philosopher. A philosopher may eat if he can pickup the two chopsticks adjacent to him. One chopstick may be picked up by any one of its adjacent followers but not both. This problem involves the allocation of limited resources to a group of processes in a deadlock-free and starvation-free manner.
- Readers and Writers Problem:
Suppose that a database is to be shared among several concurrent processes. Some of these processes may want only to read the database, whereas others may want to update (that is, to read and write) the database. We distinguish between these two types of processes by referring to the former as readers and to the latter as writers. Precisely in OS we call this situation as the readers-writers problem. Problem parameters:- One set of data is shared among a number of processes.
- Once a writer is ready, it performs its write. Only one writer may write at a time.
- If a process is writing, no other process can read it.
- If at least one reader is reading, no other process can write.
- Readers may not write and only read.
- One set of data is shared among a number of processes.
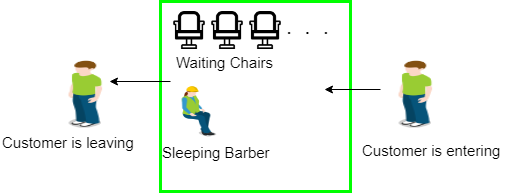
- Sleeping Barber Problem:
Barber shop with one barber, one barber chair and N chairs to wait in. When no customers the barber goes to sleep in barber chair and must be woken when a customer comes in. When barber is cutting hair new customers take empty seats to wait, or leave if no vacancy.